what can i do to get my eustachian tubes to drain
Overview
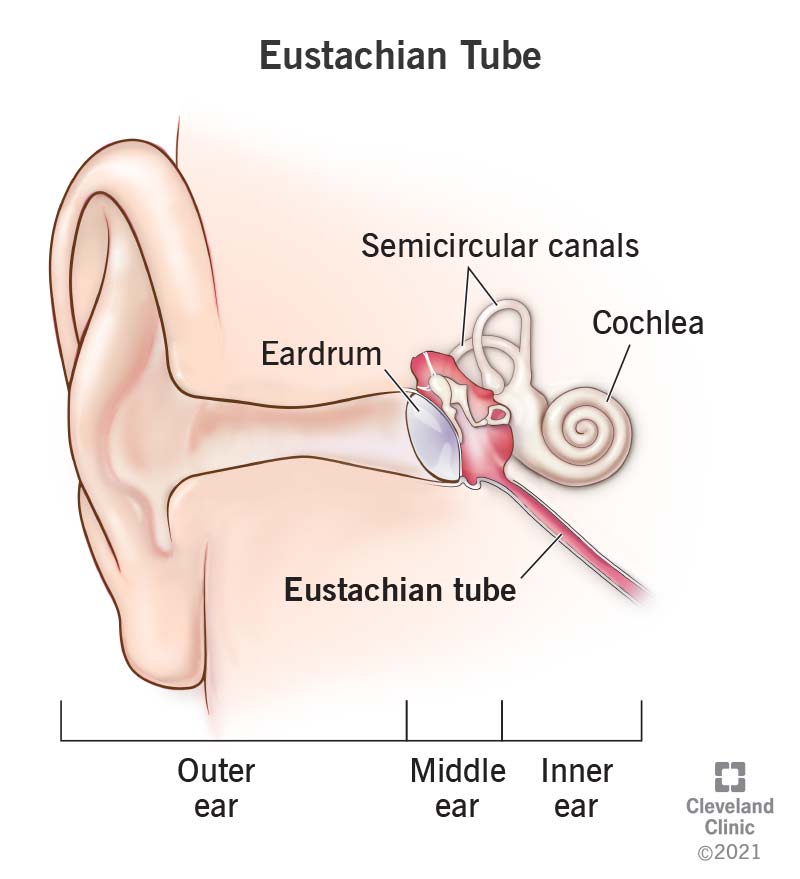
What are Eustachian tubes?
Eustachian (y'all-\_ stay\-shee-un) tubes run from the middle ears to the back of your nose and throat. They're located on each side of your face. Most of the time, your Eustachian tubes stay closed. But when you yawn, chew or swallow, they open. The Eustachian tube is named after Bartolomeo Eustachi, the Italian physician who discovered that the tube connected the middle ear to the nose and pharynx.
Function
What do Eustachian tubes do?
Your Eustachian tubes take three primary functions. They:
- Bleed excess fluids and secretions from your middle ear.
- Ventilate your eye ear and equalize air pressure on either side of the eardrum.
- Protect your middle ear from pathogens (microorganisms that cause disease).
Proper Eustachian tube function helps maintain overall ear health, including your sense of hearing.
What is actually happening when my ears "pop"?
If your ears "popular" when you yawn, you're actually hearing the Eustachian tubes open up. They do this to equalize the pressure level in your middle ear with the exterior air pressure.
Beefcake
Where are the Eustachian tubes located?
Your Eustachian tubes extend from your heart ear to the upper function of your pharynx, just behind the nose.
What does the Eustachian tube look like?
The Eustachian tube is a hollow canal that runs about 36mm in length. The first 12mm, nearest to the middle ear, is fabricated of bone. The remaining 24mm, closest to the nose and throat, is made of elastic fibrocartilage (tough, flexible cartilage).
Atmospheric condition and Disorders
What are the common disorders affecting the Eustachian tubes?
If your Eustachian tubes don't office properly, it can result in fluid buildup, ear pressure or ear pain. Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) may be associated with ear infections. The most common ETDs include:
- Patulous ETD.
- Obstructive ETD.
- Baro-claiming-induced ETD.
Patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction
This condition occurs when your Eustachian tubes stay open. When this happens, sound may travel from the nasal cavity to the ears, causing you to hear your own breathing or your ain vocalization too loudly. You might even hear your own blood pumping.
Caused past chronic nasal allergies, weight loss, GERD (chronic acid reflux) or neuromuscular diseases, patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction is often resolved with nasal drops. Or, your symptoms may improve if y'all potable more water or limit caffeine and decongestants. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to right the upshot.
Obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction
This condition occurs when your Eustachian tubes don't open up properly. As a event, fluid may build upwardly in your ears and you may feel hurting or pressure. Many people with obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction experience deadened hearing as well.
Obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction tin be caused by environmental allergies, acrid reflux, sinusitis or abnormal tissue growth, such as ear tumors. You lot may exist able to ease your symptoms by taking medication and avoiding triggers. Some people might need surgery, which may include balloon dilation of the Eustachian tube, adenoid removal, placement of ear tubes or tissue mass removal. Advisable treatment depends on the cause of the dysfunction.
Baro-challenge-induced Eustachian tube dysfunction
This condition is similar to obstructive ETD — it occurs when the Eustachian tubes don't open properly. Withal, people with baro-challenge-induced ETD only develop symptoms when traveling by airplane, scuba diving, driving through the mountains or engaging in other activities that involve atmospheric force per unit area changes.
Like obstructive ETD, treatment for baro-claiming-induced ETD depends on the crusade. However, research has indicated that airship dilation of the Eustachian tube is highly effective for military machine pilots and divers with the condition.
What are some common Eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms?
If you have Eustachian tube dysfunction, you may develop a range of uncomfortable symptoms, including:
- A feeling of fullness in your ears.
- Muffled sounds or distorted hearing.
- Popping or clicking sensations.
- Ear pain on ane or both sides.
- Ringing in your ears (tinnitus).
- Residuum problems or dizziness.
What are some mutual tests to check the health of the Eustachian tubes?
If you're showing signs of Eustachian tube dysfunction, your healthcare provider will examine your ear drum to see if it'due south functioning properly. They may also run tests to measure out the pressure level inside your ear.
What are some common treatments for the Eustachian tubes?
In many cases, Eustachian tube dysfunction goes away on its ain. Conservative treatments, such as taking medication and avoiding triggers, are oftentimes helpful. Severe or chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction may require surgery.
Continue in listen that even though antihistamines and decongestants may work for some people, they tin actually make Eustachian tube dysfunction worse in some cases. If you lot've had symptoms for longer than a week, call your healthcare provider. They can help you determine the appropriate form of activity.
Care
How can I encourage a clogged Eustachian tube to bleed?
If you have small-scale symptoms of a clogged Eustachian tube, you may exist able to clear it with some elementary exercises:
Eustachian tube massage
Use your finger to find a bony bump backside your ear lobe. Using firm, steady pressure, slide your finger down until y'all feel a groove between your ear lobe and jaw. Trace that groove all the way down your neck to your collarbone using the same house force per unit area. Repeat this process iii times on each side, iii times a day.
Valsalva maneuver
Pinch your nostrils, shut your mouth and push air out, like you're bravado up a balloon. Exercise not blow as well forcefully, however, as yous could rupture your eardrum. People with high blood pressure or those at run a risk for stroke or heart attack should not attempt the Valsalva maneuver.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your Eustachian tubes help keep your center ear healthy. Allergies, colds or infections can cause Eustachian tube dysfunction, which tin lead to hurting, dizziness, hearing issues and other problems. Most of the time, ETD goes away on its own. Just if you have symptoms that last longer than two weeks, schedule a visit with your healthcare provider. They tin determine the crusade of the trouble and design a personalized treatment plan.
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22072-eustachian-tubes
ارسال یک نظر for "what can i do to get my eustachian tubes to drain"